When we talk about "casting", we often think of roaring factories, heavy machine tools and large industrial components. But few people know that in the medical field dedicated to safeguarding health, advanced precision casting technology is quietly manufacturing "life castings" that can be "implanted into the body" or "used on the operating table" — from dental implants replacing missing teeth, to artificial hip joints rebuilding joint function, and to precision microsurgical instruments. These medical devices closely related to life and health are all empowered by casting technology. Today, we focus on these life - related medical "precision castings" and reveal how casting, with its "micron - level precision" and "excellent biocompatibility", has become a "behind - the - scenes hero" in protecting health.
1. Casting: The "Molding Code" for Medical "Precision Castings"
The requirements for medical device components are extremely strict: they must have safety compatible with human tissues, achieve dimensional accuracy at the millimeter or even micron level, and possess stable mechanical properties. And advanced precision casting technology is precisely the core process to meet these requirements.
The core advantage of this process lies in "near - net shaping" — castings can reach high precision without a lot of machining, avoiding material waste and machining stress. At the same time, it can perfectly replicate complex structures (such as the threads on the surface of implants and the curved surfaces of joints), which is exactly the "precision and delicacy" urgently needed by medical devices. Relying on its ultimate control over details and stable presentation of material properties, casting has become the preferred process for manufacturing medical precision components, laying a solid foundation for the safe application of various subsequent medical devices.
2. Dental Implants: Cast "Tooth Roots" Taking Root in the Oral Cavity
For people with missing teeth, dental implants are a hope to "regain chewing function". This seemingly simple "metal tooth root" is actually a "precision masterpiece" of casting. Its surface texture, dimensional accuracy and biocompatibility directly determine the success rate of implantation.
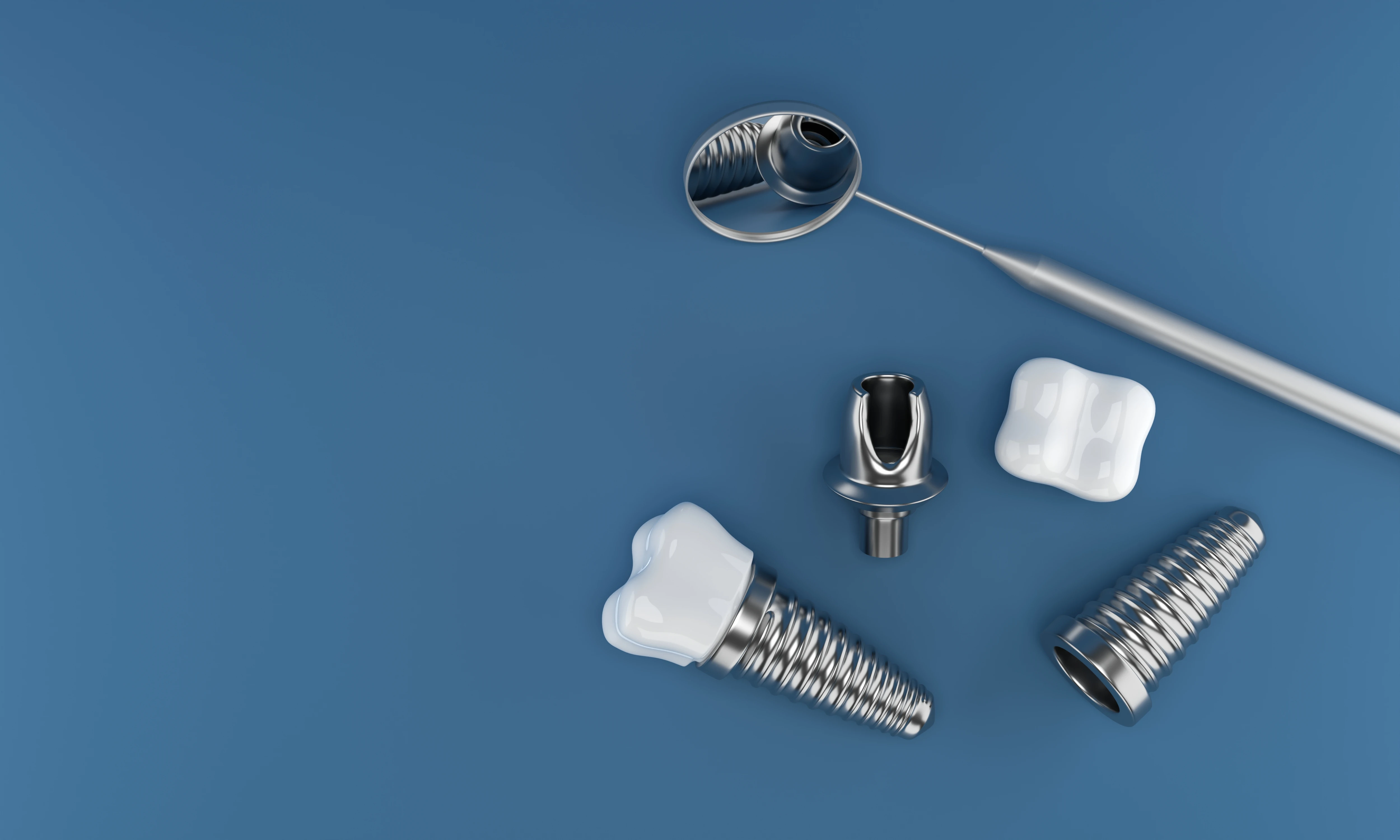

"Rooting Ability" Endowed by Casting
- Micron - level thread accuracy: The threads on the surface of the implant are the key to "taking root" in the alveolar bone. Casting can control the pitch error of the threads within ±0.02mm, and the tooth profile accuracy reaches IT5 level, ensuring that the implant is evenly stressed when screwed into the alveolar bone and not easy to loosen;
- Rough surface texture: Through special casting processes, a micron - level rough texture (Ra5 - 10μm) is formed on the surface of the implant. This texture can increase the contact area with bone tissue, promote the attachment and growth of osteocytes, shorten the osseointegration time from the traditional 3 - 6 months to 1 - 2 months, and increase the implantation success rate to more than 95%.
Transformation from Casting to "Real Tooth"
The cast implant blank needs to undergo surface treatments such as sandblasting, pickling and polishing to remove the oxide layer and further optimize the surface roughness. Finally, after being implanted into the oral cavity, it can bear chewing force like a natural tooth (a single implant can bear a biting force of 300 - 500N, which is equivalent to the force of biting an apple), allowing patients to regain a natural chewing experience.
3. Artificial Joints: Cast "Hubs" for Rebuilding Motor Function
For patients with severely damaged joints due to arthritis or trauma, artificial joint replacement surgery is a "lifesaver" to restore motor function. The core components of artificial hip joints, knee joints, etc., are exactly the "precision movement hubs" created by casting. Their surface finish, joint clearance and wear resistance directly affect the quality of life of patients after surgery.
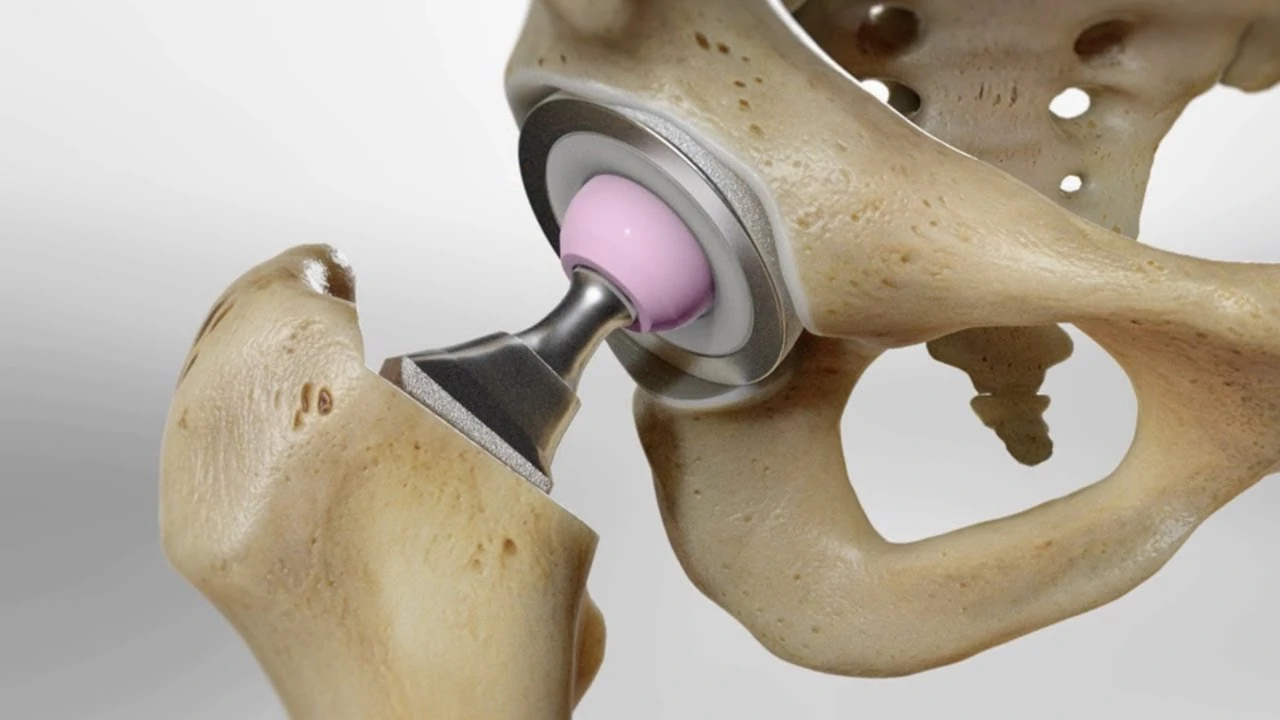
"Joint Wisdom" of Casting
The key components of artificial joints (such as the femoral head of the hip joint and the tibial plateau of the knee joint) are mostly made of cobalt - chromium alloy or ceramic - metal composite materials through casting. Casting technology plays an irreplaceable role here:
- Precise forming of complex curved surfaces: The joint surface of the artificial joint is a complex curved surface conforming to human engineering, requiring a surface finish of Ra ≤ 0.8μm (equivalent to the mirror level). Advanced casting processes ensure smooth mold surfaces that can perfectly replicate the curved surface accuracy of the original pattern, reduce the subsequent machining amount, and avoid the damage to the joint surface accuracy during the machining process;
- Lightweight internal structure: Through casting, a hollow structure can be designed inside the joint stem to reduce weight while ensuring strength (the weight of the artificial hip joint can be controlled at 100 - 150g), reducing the limb burden of patients after surgery and making walking more natural;
- Enhanced wear resistance: After heat treatment, the surface hardness of cobalt - chromium alloy castings can reach HRC30 - 35. Cooperated with ultra - high molecular weight polyethylene liners, the wear rate is extremely low (only 0.1mm or less per year), and the service life of artificial joints can be as long as 15 - 20 years, benefiting patients for a long time.
Behind "Walking Freely"
Taking the artificial hip joint as an example, the matching clearance between the cast femoral head and the acetabular cup needs to be controlled at 0.05 - 0.1mm to ensure smooth and non - stuck joint movement. After surgery, patients can not only walk normally and go up and down stairs but also engage in light sports such as swimming and cycling, returning to normal life.
4. Surgical Instruments: Cast "Sharp Tools" for Precision Operation
On the operating table, the surgical instruments in the doctor's hands are weapons for "treating diseases and saving lives". From tweezers and scissors to needle holders and dissectors for microsurgery, many key components of these precision instruments rely on casting to achieve the unity of "small and flexible" and "firm and durable".
"Surgical Precision" Endowed by Casting
Surgical instruments are mostly made of medical stainless steel (such as 316L stainless steel) through casting. Casting technology gives them two advantages:
- Forming of microstructures: The tip width of microsurgical instruments (such as tweezers used in ophthalmic surgery) is only 0.1 - 0.2mm. Precision casting can accurately form such microstructures, and the edges are sharp without burrs, avoiding tissue damage during surgery;
- High strength and corrosion resistance: After solution treatment, the cast stainless steel instruments can have a tensile strength of more than 550MPa, which can withstand bending and torsion forces during surgery without deformation. At the same time, 316L stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high - temperature and high - pressure sterilization (134℃, 0.2MPa), and its performance remains unchanged after repeated sterilization, ensuring surgical safety.
Guarantee for "Effective Treatment with Skillful Hands"
For example, the brain spatula used in neurosurgery. The arc spatula made by casting has a smooth surface and can accurately separate brain tissue without causing damage; the intramedullary nail aiming device used in orthopedic surgery has a casting positioning hole accuracy of ±0.1mm, ensuring the accurate implantation position of the intramedullary nail and reducing surgical trauma. These "cast sharp tools" are important helpers for doctors to complete precise operations.
5.Casting and Medicine: Guardian from "Precision" to "Life"

From the implants in the mouth, to the "hubs" in the joints, and then to the "sharp tools" on the operating table, these "precision castings" hidden in the body or active in medical scenarios are backed by the ultimate pursuit of "precision" and "safety" by advanced casting technology. It not only realizes the "shape" of medical devices but also endows them with "biocompatibility" — allowing metals to coexist harmoniously with the human body and making devices reliable partners in protecting health.
With the continuous development of medical technology, the requirements for medical devices are getting higher and higher: lighter and thinner structures, better biocompatibility, and more precise functions. And casting technology is also constantly innovating, from traditional precision casting to rapid prototyping technology combining 3D printing and casting, from single metal materials to metal - ceramic composite materials. The "bond" between casting and medicine will become deeper and deeper, bringing more possibilities for human health.
Next time when you or people around you are exposed to dental implantation, joint replacement or surgical treatment, you might as well think about these "precision castings hidden in the body" — they may be unknown, but they use the "craftsmanship" of casting to guard every vivid life.
Conclusion
Although medical precision castings are often small in size or hidden in the human body, they play an "irreplaceable" role in safeguarding health - from the "rooting" stability of dental implants in the oral cavity to the flexible movement of artificial joints in the limbs; from the precise operation of microsurgical instruments on the operating table to the biocompatible coexistence with human tissues. These castings operate reliably in the special "medical environment" with the advantages of micron-level precision, excellent biocompatibility, and complex structure replication, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical treatments.
When developing medical castings, the core is to match materials and processes according to clinical needs (such as implantation site, load-bearing requirements, biocompatibility standards), while considering long-term service performance and sterility requirements. If you have questions about "material selection of medical castings for specific implantation scenarios" or "application prospects of casting technology in new medical devices", please leave a message in the comment area, and we will provide you with professional answers!







